Developing #Listening Skills – Music Fun

These games are designed to help a child learn about the different levels of sound, pitch, tone and volume.
Music Fun
- Skittle Band – Use, or make, a drum stick (wooden spoons are good for this) and explore with your child the different sounds the drum stick makes against objects made of different materials, such as steel saucepan, another wooden spoon, plastic bottles etc. Choose items that are safe and you are happy for them to play with. You could photograph the objects, record the sounds they make, or video (on your phone), to play back and talk about later on. Try moving the activity outside for a different sound quality experience.
- Orchestral Conductor – Once your child is happy and enjoys playing and making sounds, with different objects and instruments, try the conductor game. You can use your hands or a baton to point and encourage them to play certain sounds just like an orchestral conductor does, but make sure you have a clear stop gesture which your child will understand (you may need to say stop at the same time as the gesture to begin with, but they will soon get the idea). Then swap places and you become the musician and they the conductor; it may not be a classic you create but it is great fun. As your child develops their skills you can add new elements and hand gestures to make the sound louder or softer.
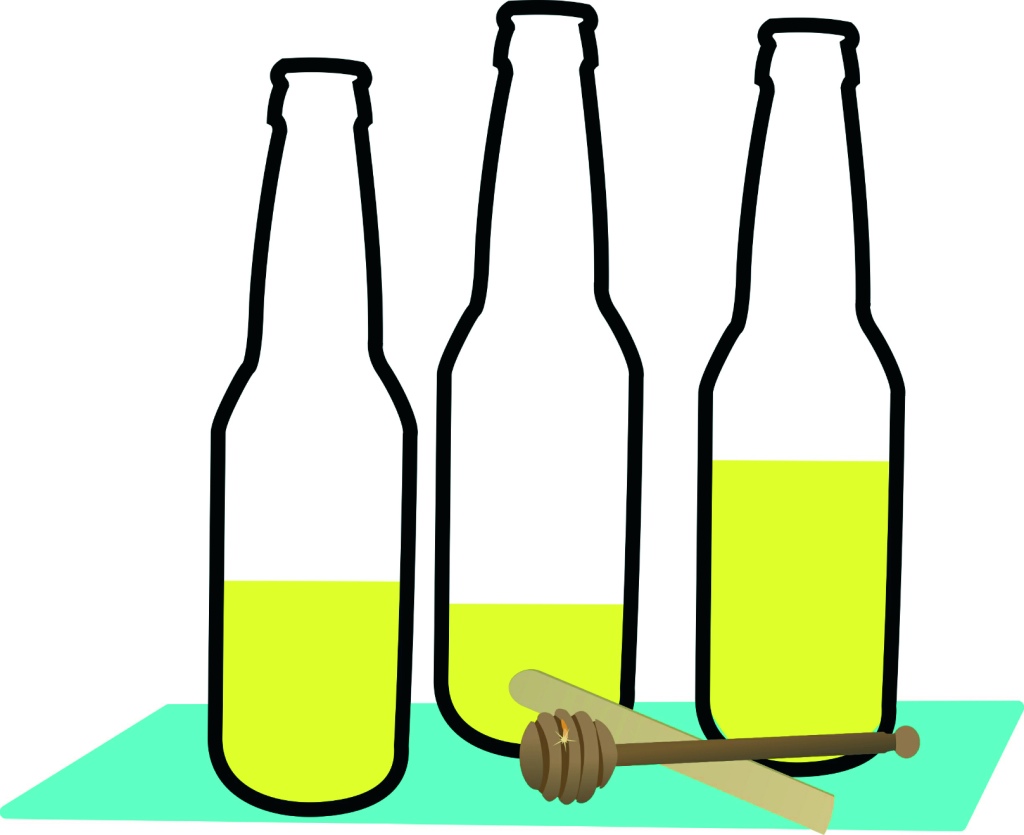
- Musical Bottles – Use plastic bottles with different amounts of water/sand in them and different things as a beater. Talk about how:
- Low/deep or high pitched a sound is compared with another.
- Using different beaters can change the quality of the sound when used on the same bottle.
- Using different amounts of pressure to hit the bottle makes the sound louder (harsher) or quieter (softer).
Try organizing the bottles in order of pitch to create a musical instrument and using this as part of the Orchestral Conductor game. You could number each bottle or use a different picture on the bottle as a way of encouraging your child to play the bottles in different orders (making music).