Here at Teach Children we have always promoted the importance and power of teaching the correct letter names to begin with; through our Teach Handwriting website, Schemes and Teach Phonics website. Unfortunately, some schools, teacher and parents still seem to be concerned that this is not consistent with the teaching of phonics, which is just not correct.
A myth which became popular, in the early years of introducing synthetic phonics into schools, is that children should not be taught the alphabet letter names as they find it too confusing. However, in recent years this has started to change as phonics schemes have adjusted some of their approaches to teaching phonics to include the use of letter names.
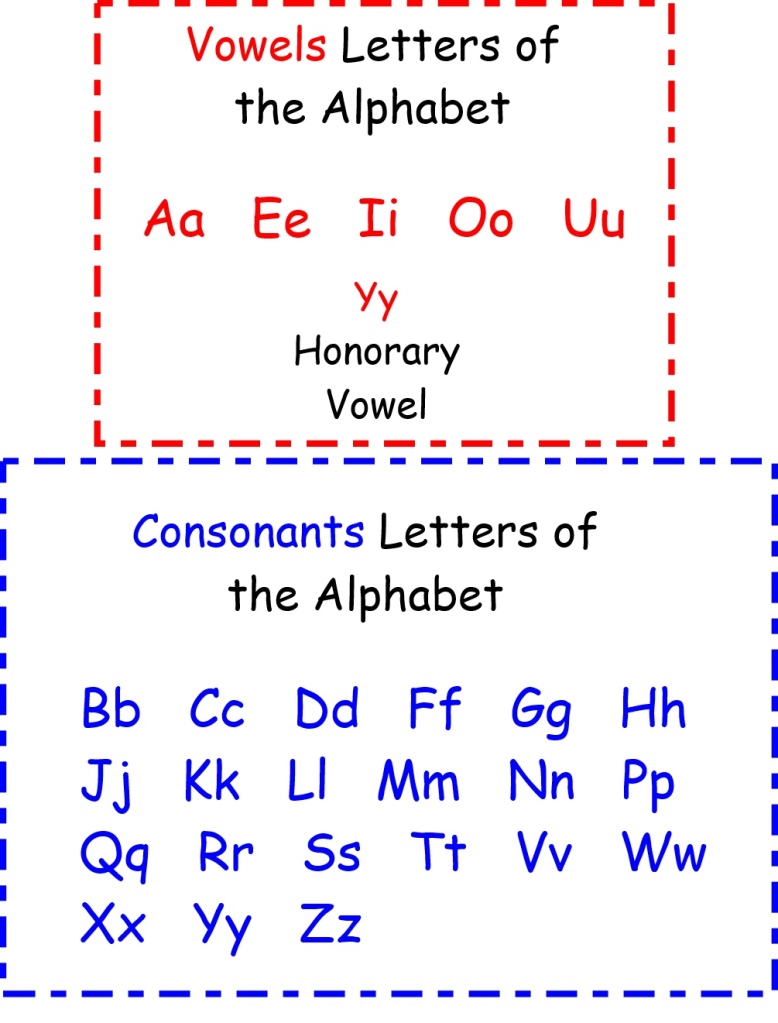
Learning the unique letter names of the alphabet is a pre-phonics skill; as well as an early learning goal. It has to be remembered that a letter is a shape which only represents a sound when it is placed within a word or sentence (has a context). Also, a letter or combination of letters can represent more than one sound and so the only unique way of identifying alphabet letters when we talk about them is to use their names.
It is important to remember that just because a child can correctly recite the ‘Alphabet’ song it does not mean they know the letters of the alphabet. It is surprising how many children can do this but when shown letters from the alphabet cannot name them at all. They may be able to tell you the sound the letter makes but have no idea of the letters name.
Learning the correct letter names helps to reinforce that when talking about the letter ‘a’ (ay) for example it has a set shape regardless of the sound that it will be representing in the word. This further supports children’s handwriting development as the communication of your requirements is unambiguous.
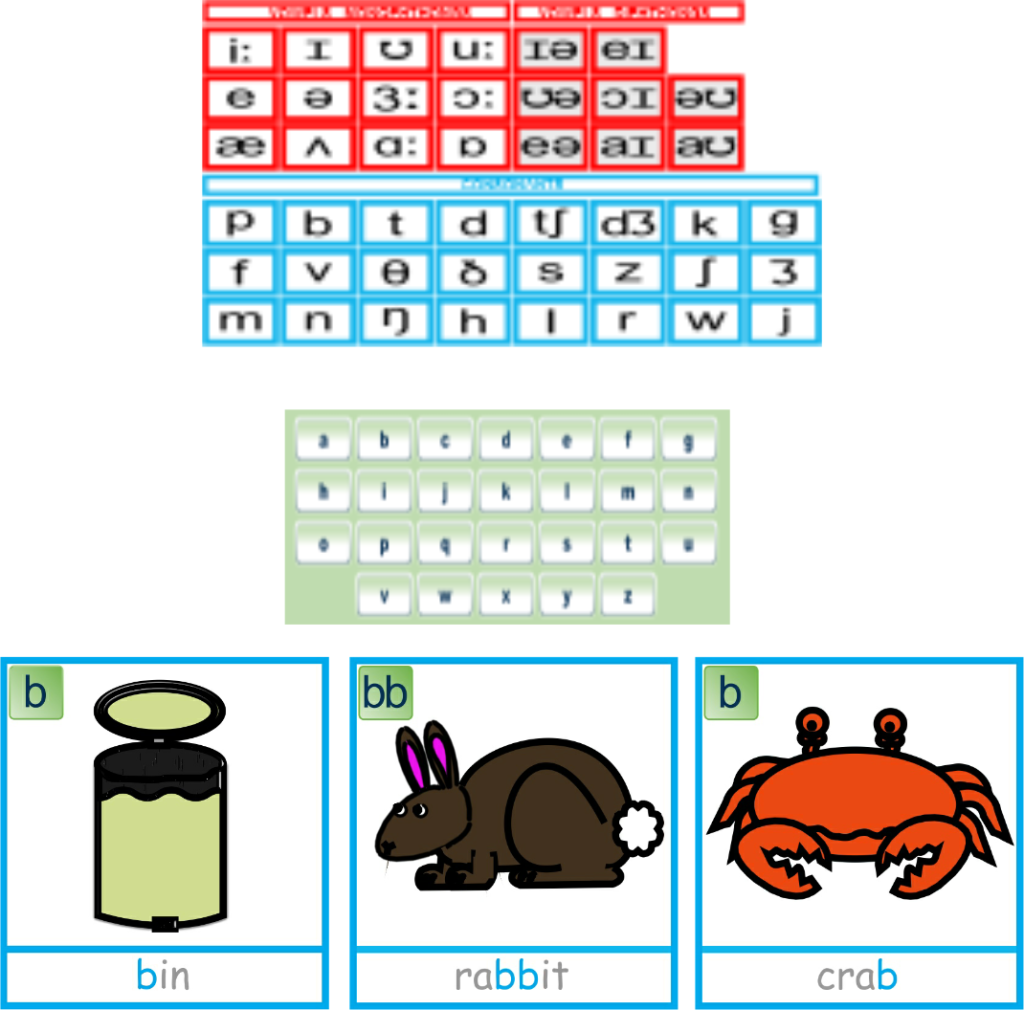
Teaching the correct letter names is important when supporting handwriting as this can in turn affect a child’s phonics understanding later on. For example, it can seem very easy when explaining to a child which letter to write when they ask which one is making a ‘kuh’ sound in a word such as cat to say a ‘curly kuh’. There is no such letter in the alphabet called ‘curly kuh’ it is the letter ‘c’ (cee). By adding the ‘kuh’ sound to the letter it reinforces incorrect phonics knowledge. The letter ‘c’ does not make a ‘kuh’ sound in words such as: city, circle, cycle and centre.
Some children will then only ever refer to the letter ‘c’ as ‘curly kuh’ and the letter ‘k’ as’ kicking kuh’. As I say these are not letter names of the alphabet and also devalue the power of phonics at the same time.
How can the education establishment get hot under the collar about not using the correct terminology in the teaching of English in schools such as: phonemes, graphemes, digraphs, modal verbs etc… yet still refer to the letter’s ‘c’ and ‘k’ as ‘curly or kicking kuh’!
Phonics is a powerful decoding and encoding tool. However, so is the alphabet letter naming system. Both need to working side by side to support our children, especially in those early years of their educational journey.
The English phonic system is very complex but this is why our language is so rich. Young children need to use letter names as an additional tool, as it takes many years for them to be introduced to the more complex phonics coding system.
Alphabet Name animation (scroll to the bottom of the page): https://www.teachphonics.co.uk/phonics-graphemes.html