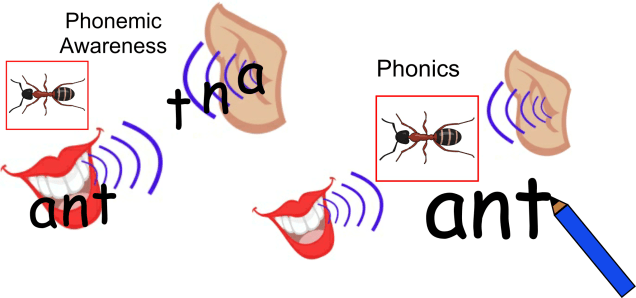
With many parents sadly having to tackle home learning again; we thought it would be useful to re-run this blog from last year explaining CVC words in phonics.
The letter C means a consonant letter is required.
The letter V means that a vowel letter is required.
So, a CVC word is one that has a consonant letter followed by a vowel and then a consonant as in the following examples:
cat dog mat
There are 26 letters in the English alphabet and these can be split in to two categories:
Vowels – ‘a’, ‘e’, ‘i’, ‘o’, ‘u’ and the letter ‘y’, when it is used as a semi-vowel, in words such as by, my and fly.
Consonants – ‘b’, ‘c’, ‘d’, ‘f’, ‘g’, ‘h’, ‘j’, ‘k’, ‘l’, ‘m’, ‘n’, ‘p’, ‘q’, ‘r’, ‘s’, ‘t’, ‘v’, ‘w’, ‘x’, ‘z’ and the letter ‘y’ when it is being used as a consonant, in words such as yak, yam and yellow.
Schools will often use the abbreviation CV, CVC, CVCC words when sending home phonics work or suggestions for phonics games. It is also used by many phonics computer games, activity programs and schemes.
Here are some examples for: