[For a pdf copy of this diagram click here]
PDF: https://www.teachphonics.co.uk/assets/pdfs/the-simple-view-of-reading.pdf
The term ‘Simple View of Reading’ used by schools may seem strange as there is nothing simple about learning to read.
‘The Simple View of Reading’ was adopted by the Government in 2007 and now underpins the English National Curriculum’s programmes of study for reading at Key Stage 1 and 2.
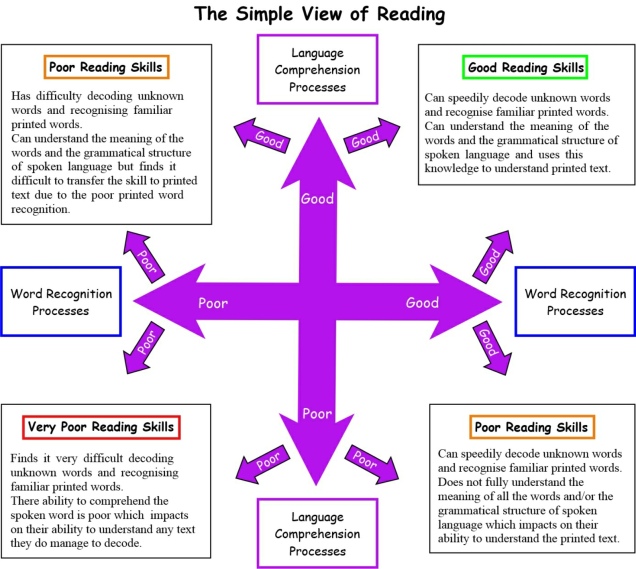
Even though reading, the ability to decode the word and extract the correct meaning of the words, is a complex set of skills; ‘the Simple View of Reading’ conceptual framework (Stuart et al. 2008, cited Hoover and Gough, 1986) reduces it down to two key components:
- Word recognition – the ability to decode unknown words and recognise printed words.
- Language comprehension – the ability to understand the spoken words and use this process to understand the written text.
| Reading Comprehension = Decoding x Linguistic Comprehension |
So in theory a child’s reading comprehension ability can be predicted by looking at their decoding and linguistic (spoken language) comprehension abilities (Johnston & Watson, 2007).
When using ‘the Simple View of Reading’ as the basis for teaching reading it becomes clearer as to why:
- A high quality phonics scheme is required, which the Rose Report (2006) explains ‘…is not a ‘strategy’ so much as a body of knowledge, skills and understanding that has to be learned.’ (page 20) [This teaches children how to decode.]
- A language rich environment to develop and encourage linguistic comprehension is vital.
Bibliography
Johnston.R. and Watson.J. ‘Teaching Synthetic Phonics’, 2007, Pub: Learning Matters, Sage Publication Ltd.
Rose.J. ’Independent review of the teaching of early reading: final report March 2006’ Pub: DfES Publications
‘The simple view of reading and evidence based practice’ Rhona Stainthorp Institute of Education, Reading University, Morag Stuart, Institute of Education, University of London (2008) Pdf downloaded from internet