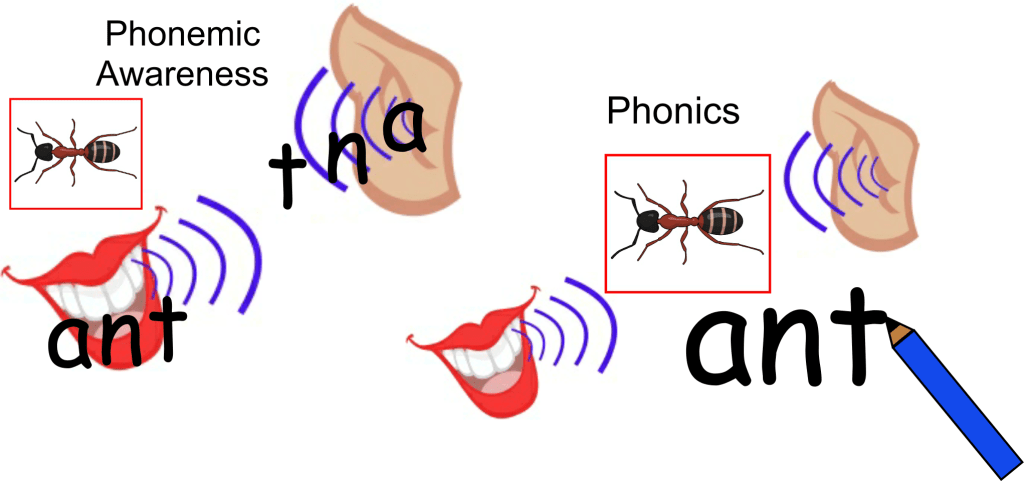
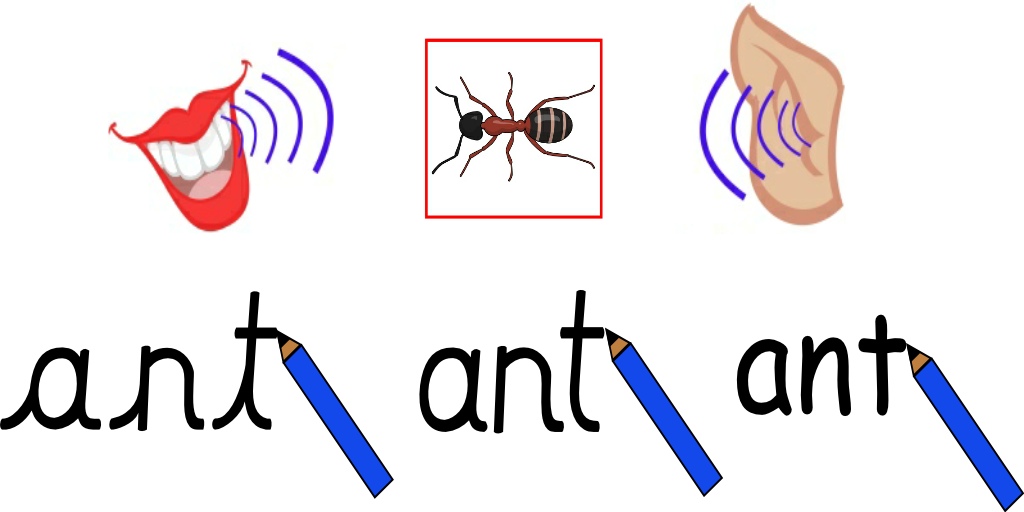
Last week we started to explain some of the technical language associated with the teaching of phonics, which some new parents may have little or no knowledge of. So, we thought it would be a good idea to continue with this over next couple of weeks to further support you in helping your child.
Graphemes are the alphabet letters, or letter combinations, that represent a single sound (phoneme) in a written word.
An example of a single letter (grapheme) representing a single sound (a phoneme) can be seen in the following words: sat, pat and dog.
Some sounds are represented by two letters and are called digraphs such as the ‘ch’ in ‘chip’ or ‘sh’ in ‘shop’ or ‘ea’ in ‘head’ and the ‘ai’ in ‘rain’.
Other sounds can be represented by 3 (trigraphs) or 4 (quadgraphs) letter combinations such as ‘igh’ in ‘light’ and ‘eigh’ in ‘eight’.
Phonemes are the smallest units of sound of a language; which we blend together to form words.
The English Language has 44 phonemes, 24 consonants and 20 vowels, represented by the unique symbols of the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA).
The 44 phonemes of English (UK) are represented by more than 280 letter or letter combinations. Most letters therefore never make just one sound and that sound can be made by more than one letter or letter combination.
We have created over 1,000 videos that split words into their individual phonemes, showing which letters are making which sound in each word. You can access these videos in two ways:
- If you want to know which letter or letter combination represents a sound, click on the relevant phoneme button on the English Phoneme Chart: https://www.teachphonics.co.uk/phonics-phomene-chart.html;
- If you want to know what sound a letter or letter combination makes and see supporting animations, click on the relevant letter or letter combination on the Alphabet Keyboard: https://www.teachphonics.co.uk/phonics-alphabet-chart.html
We hope you find these useful.